What is an Inverted Yield Curve, and What Does it Mean to Me?
October 2, 2019
In early August of 2019, headlines referring to the feared “inverted yield curve” were on display all over the news, financial websites, and publications, sparking a more than 2.9% decline in the S&P 500 (Source: Yahoo Finance), its worst single day of trading for the year.
The following day, a plethora of articles were published explaining an inverted yield curve and linking its direct correlation to an imminent recession, further weakening investor sentiment. In this day and age where the headlines are often times scary, many are wondering: what is an inverted yield curve and linking its direct correlation to an imminent recession, further weakening investor sentiment. In this day and age where the headlines are often times scary, many are wondering: what is an inverted yield curve and should they panic?
Why is the inverted yield curve important?
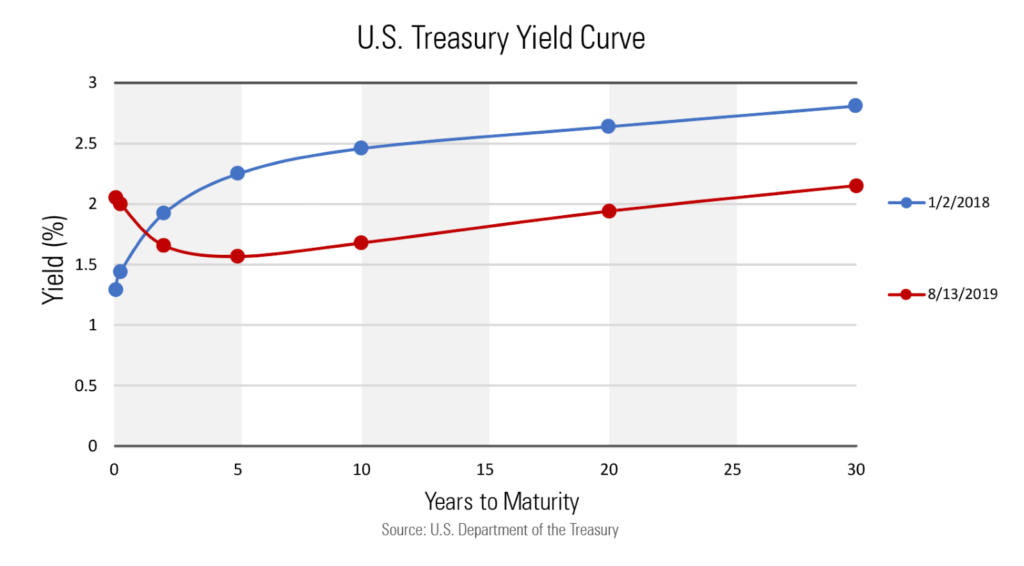
An inverted yield curve simply occurs when shorter-term interest rates are higher than longer-term rates. A good way to understand this is by using an example of a certificate of deposits (CD’s). If you purchase a six-month CD, you would expect the interest rate would be less than a three-year CD. However, when the yield curve inverts it, the shorter-term CD is earning higher interest than the longer-term. This situation, which rarely occurs, has historically been a dependable indicator of a recession. On average, a recession occurs 18 months after the yield curve inverts.
Why does the yield curve invert?
At the short end of the curve, the Fed exercises direct control by raising and lowering the federal funds rate. The long end of the yield curve gets complicated, though, as it is influenced by investors’ expectations, specifically market sentiment and inflation expectations. Generally speaking, if investors believe the economy is going to face headwinds in the future, they will purchase longer term bonds which will cause longer-term interest rates to decline.
Should I be concerned about the inverted yield curve?
So, because you are now familiar with what an inverted yield curve is, now comes the question you are really wondering; what effect will an inverted yield curve have on my investments? There isn’t a simple answer, but historical data shows us that the results aren’t nearly as gloomy as media outlet headlines would lead you to believe. Let’s say the inverted yield curve does lead to a recession sometime in the next 12-24 months, would it be wise to move all your investments to cash? Gold? Under your mattress? The answer is most likely no. During the last 14 recessions in the U.S., stocks returned on average +1.2% while U.S. bonds returned +8.2% (Source: Morningstar). However, it’s important to note that these returns could have been much worse if an investor wasn’t properly diversified.
What tips should I follow in dealing with the inverted yield curve?
Recessions are an inevitable part of the business cycle and investors should be careful to maintain proper asset allocation in their portfolios, rather than trying to make tactical moves in an attempt to time market swings or predict significant economic events. It’s important to remove emotions from the investing process, this is admittedly even more difficult in today’s world of information overload. It’s almost impossible to escape the unsettling headlines. But in order to build and preserve your nest egg, it’s imperative to keep calm and remain diversified. In the wise words of famed investor Benjamin Graham, “The investor’s chief problem – and even his worst enemy – is likely to be himself.”
Let the Certified Financial Planner® professionals at Williams Asset Management help with your wealth management needs. Whether you need comprehensive and holistic financial planning or investment management, we can help! We are fee-based, independent financial advisors located in Columbia, the heart of Howard County, Maryland. Schedule your complimentary consultation today by calling (410) 740-0220!


